Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol for network discovery on the data link layer. It can share information such as device names and IOS versions, with other physically connected Cisco devices. Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is vendor-neutral protocol using on the data link layer for network discovery. It is mainly used with network devices in the local area network (LAN). The network devices advertise information, such as their identities and capabilities to their neighbors.
Cisco Discovery Protocol – CDP
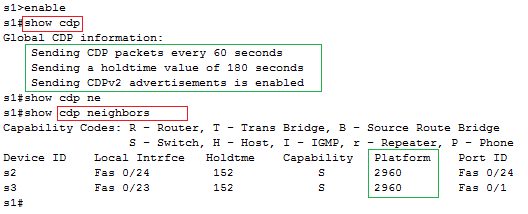
CDP discovers basic information about neighboring routers and switches without needing to know the passwords for the neighboring devices. To discover information, routers and switches send CDP messages out each of their interfaces. The messages essentially announce information about the device that sent the CDP message. Devices that support CDP learn information about others by listening for the advertisements sent by other devices.
CDP discovers several useful details from the neighboring Cisco devices:
- Device identifier: Typically the host name
- Address list: Network and data-link addresses
- Port identifier: The interface on the remote router or switch on the other end of the link that sent the CDP advertisement
- Capabilities list: Information on what type of device it is (for example, a router or a switch)
- Platform: The model and OS level running on the device
CDP plays two general roles: to provide information to the devices to support some function and to provide information to the network engineers that manage the devices. For example, Cisco IP Phones use CDP to learn the data and voice VLAN IDs as configured on the access switch. For that second role, CDP has show commands that list information about neighboring devices, as well as information about how CDP is working. Below image describes the three show commands that list the most important CDP information.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
show cdp neighbors [type number] | List one summary line of information that about each neighbor or just the neighbor found on a specific interface if an interface was listed. |
show cdp neighbors detail | List one large set (approximately 15 lines) of information, one set for each neighbor. |
show cdp entry name | list the same information as show cdp neighbors detail command, but only for the named neighbor. |
Configuring and Verifying CDP
Most of the work you do with CDP relates to what CDP can tell you with show commands. However, it is an IOS feature, so you can configure CDP and use some show commands to examine the status of CDP itself. IOS typically enables CDP globally and on each interface by default. You can then disable CDP per interface with the no cdp enable interface subcommand and later reenable it with the cdp enable interface subcommand. To disable and re-enable CDP globally on the device, use the no cdp run and cdp run global commands, respectively.
Link Layer Discovery Protocol – LLDP
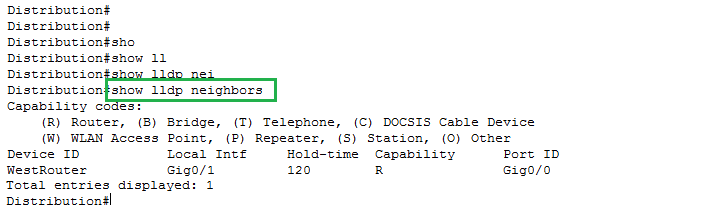
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral link layer protocol, defined in IEEE standard 802.1AB, provides a standardized protocol that provides the same general features as CDP. LLDP has similar configuration and practically identical show commands as compared with CDP.
Both the show cdp neighbors and show lldp neighbors commands have “local intf” (interface) and “port ID” columns. These columns refer to the local device’s interface and the neighboring device’s interface, respectively. However, the LLDP output in the example does differ from CDP in a few important ways:
LLDP uses B as the capability code for switching, referring to bridge, a term for the device type that existed before switches that performed the same basic functions.
LLDP does not identify IGMP as a capability, while CDP does (I).
CDP lists the neighbor’s platform, a code that defines the device type, while LLDP does not.
LLDP lists capabilities with different convention.
LLDP Media Endpoint Devices (LLDP-MED)
LLDP-MED is an extension to LLDP. This protocol is specifically used to support Voice Over IP (VOIP) applications. LLDP-MED enables network discovery between network connectivity devices and media endpoints such as, softphones, IP telephones, VOIP gateways and conference bridges. By default, network devices sends out only LLDP packets until it receives LLDP-MED packets from an endpoint device. It will then keep sending out LLDP-MED packets until the remote device to which it is connected to ceases to be LLDP-MED capable. It supports the following TLVs:
- LLDP-MED capabilities TLV
- Network policy TLV
- Power management TLV
- Inventory management TLV
- Location TLV
LLDP timers
Hold timer refers to the time or duration that an LLDP device maintains the neighbor information before aging it. The default is 120 seconds. If the timer expires and no LLPD packet was received, the neighbor information will be discarded.
Frequency timer pertains to the interval at which the network devices sends LLDP updates to neighboring devices. The default is 30 seconds.
Reinit timer is the delay time for LLDP to initialize on any interface. The default is 2 seconds.
Configuring and Verifying LLDP
LLDP uses a similar configuration model as CDP, but with a few key differences. First, Cisco devices default to disable LLDP. Additionally, LLDP separates the sending and receiving of LLDP messages as separate functions. For instance, LLDP support processing receives LLDP messages on an interface so that the switch or router learns about the neighboring device while not transmitting LLDP messages to the neighboring device. To support that model, the commands include options to toggle on|off the transmission of LLDP messages separately from the processing of received messages.
LLDP is disabled by default and can be activated through the lldp run command. Listed below are the following commands that we will implement on our topology.
| lldp run | Enables LLDP on devices |
| no lldp run | Disables LLDP on devices |
| lldp {med-tlv-select tlv | receive | transmit} | Enables an LLDP-MED TLV or LLDP packet transmit/receive on an interface. |
| no lldp {med-tlv-select tlv | receive | transmit} | Disables an LLDP-MED TLV or LLDP packet transmit/receive on an interface. |
| lldp med-tlv-select | Enables specific LLDP-MED TLV on an interface |
| lldp holdtime | Sets the hold time on device; range is 0 – 65535 seconds. |
| lldp timer | Sets the rate at which LLDP packets are sent; range is 5 – 65535 seconds. |
| lldp reinit | Sets the initialization time on any interface; range is 2 – 5 seconds. |
Disabling and Enabling LLDP Globally
LLDP is enabled by default. Follow these steps to disable LLDP:
Enter global configuration mode
Issue no lldp run to disable LLDP
Return to privileged exec
Switch#conf t
Switch(config)#no lldp run
Switch(config)#end
And this is how to enable LLDP when it has been disabled:
Enter global configuration mode
Issue lldp run command
Return to privileged exec
Switch#conf t
Switch#lldp run
Switch#end
After enabling LLDP Globally on switch, we will need to specify the interfaces which we will want to enable LLDP and enter their interface configuration mode.
Switch#conf t
Switch(config)#int range fa0/1-4
Switch(config-if-range)#lldp transmit
Switch(config-if-range)#lldp receive
Switch(config-if-range)#end
You can configure the amount of time for LLDP packets to hold the information before discarding it, the frequency of LLDP updates, and the initialization delay time.
Switch#conf t
Switch(config)#lldp holdtime 120
Switch(config)#lldp reinit 2
Switch(config)#lldp timer 30
Switch(config)#end
Simply put the no form of each of the LLDP commands to return to the default setting.






